Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Reflection of Light, Laws of Reflection of Light, Average Speed of Image in Concave Mirror & Focal Plane of a Spherical Mirror etc.
Important Questions on Reflection at Plane and Spherical Surfaces
An object is placed at from the concave mirror of focal length the nature of the image and magnification will be
State and visualise the laws of reflection.
State and visualise the first law of reflection.
Where the origin is taken, while solving problem regarding the spherical mirror
What is the centre of curvature of spherical mirrors
A ray of light is incident towards a plane mirror at an angle of with the mirror surface.What will be the angle of reflection?
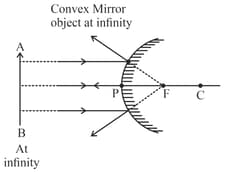
In the following, ray diagram of convex mirror,when object is placed at infinity then the nature of the image is _____________.
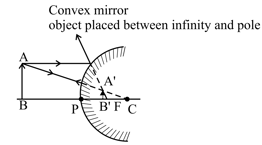
In the given ray diagram of convex mirror, when object is placed between infinity and pole then image is formed between pole and focus?
Draw the ray diagram of convex mirror,in case of when object is placed at infinity?
In a convex mirror, magnification is
In a concave mirror for real images magnification is taken in respect of heights.
When object is placed to the left side of a mirror,the object distance is always__________.
The upward distances perpendicular to the principal axis are taken as positive.
Distances measured in the direction of incident light are taken as _____, while distance measured opposite to the direction of the incident light are taken as negative.
The principal focus of a spherical mirror lie midway between the _____ and centre of curvature.
The principal focus of a spherical mirror lie midway between the pole and centre of curvature.
An object beyond the centre of curvature forms a real and _____ image between the focal point and the centre of curvature.
Is centre of curvature a part of mirror?
Centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies___________.
The transverse magnification of convex mirror is always less than .
